What is Cloud Computing?
In Cloud Computing, the word cloud is used as a metaphor for the internet, so the phrase cloud computing means services such as services are delivered to organization computers and devices through the internet.
or
Cloud Computing is a model for enabling on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources that can be rapidly released.
Follow us on Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/techtoday1212/?hl=en
See also: What is Arduino Uno Chip?
Follow us on Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/techtoday1212/?hl=en
See also: What is Arduino Uno Chip?
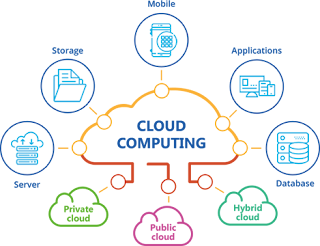
It basically stores the data, software or other applications on the cloud. Agility for organizations may be improved, as cloud computing may increase user's flexibility with re-provisioning, adding, or expanding technological infrastructure resources.
Cost reductions are claimed by cloud providers. A public-cloud delivery model converts capital expenditures (e.g., buying servers) to operational expenditure. This purportedly lowers barriers to entry, as infrastructure is typically provided by a third party and need not be purchased for one-time or infrequent intensive computing tasks. Pricing on a utility computing basis is "fine-grained", with usage-based billing options. As well, less in-house IT skills are required for the implementation of projects that use cloud computing. The e-FISCAL project's state-of-the-art repository contains several articles looking into cost aspects in more detail, most of them concluding that costs savings depend on the type of activities supported and the type of infrastructure available in-house.
SERVICE MODELS
Infrastructure as a service (IaaS)
A vendor provides clients pay-as-you-go access to storage, networking, servers and other computing resources in the cloud.
Platform as a service (PaaS)
A service provider offers access to a cloud-based environment in which users can build and deliver applications. The provider supplies underlying infrastructure.
Software as a service (SaaS)
A service provider delivers software and applications through the internet. Users subscribe to the software and access it via the web or vendor APIs.
TYPES OF CLOUD
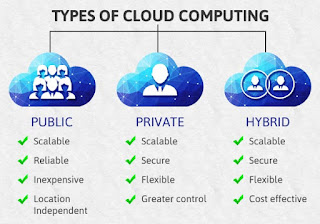
- PRIVATE/ INTERNAL CLOUD
They have a significant physical footprint, requiring allocations of space, hardware, and environmental controls. These assets have to be refreshed periodically, resulting in additional capital expenditures.
- PUBLIC/ EXTERNAL CLOUD
Public cloud services are free. Technically there may be little or no difference between public and private cloud architecture, however, security consideration may be substantially different for services that are made available by a service provider for a public audience and when communication is effected over a non-trusted network.MAINTENANCE
Maintenance of cloud computing applications is easier because they do not need to be installed on each user's computer and can be accessed from different places (e.g., different work locations, while traveling, etc.).

Comments
Post a Comment